Skin is the biggest organ in the body. It is responsible for guarding against environmental factors and effects, temperature regulation, and hydration. Due to these reasons, several diseases attack the skin, affecting not only its appearance but even one’s health in general. This article gives a summary of common skin diseases, their types, causes, symptoms, and treatment.
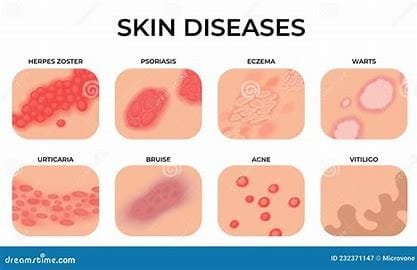
1. Types of Skin Diseases
Severe to mild, these can either be temporary or chronic; skin diseases include: Common conditions of the skin include eczema, or atopic dermatitis. This is a condition where dry and itchy inflammation results from chronic skin that particularly involves the hands, neck, face, and feet.
Psoriasis: A disease caused by an autoimmune reaction. It develops the appearance of thickened scales, which are often found in the scalp, elbows, and knees.
Acne: Acne is extremely common in both adolescents and adults and involves the blockage of hair follicles by oil and dead skin cells. Pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads can occur.
Rosacea: Rosacea is an illness where redness happens on the face and sometimes visible blood vessels plus recurrent pimples. It happens on the face but could be mistaken for acne.
Vitiligo: In this disease, the skin loses its pigmentation and leads to white patches that can appear on any part of the body.
Skin Cancer: Melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma are the other common forms. Skin cancer is one of the most common and preventable forms of cancer.
Hives (Urticaria): Red itchy swellings of skin due to food, medications, or exposure to substances in the environment.
Fungal Infections: These include ringworm, athlete’s foot, and yeast infections due to fungi that prefer to inhabit the warm and moist areas of the body.
2. Causes of Skin Diseases
The causes of skin diseases are as diverse as the conditions. Among the most common causes are:
Genetics: Many of the skin diseases, like psoriasis and eczema, have a genetic component, so they often run in families.
Allergies and Immune Reactions: Eczema, hives, and rosacea often arise from an overactive immune reaction to some allergen or environmental trigger.
Hormonal Changes: At puberty, pregnancy, or during the menopause, there can be overproduction of oil due to hormonal changes resulting in acne.
Infections: Most diseases of the skin are due to infections through various pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Among these are infections caused by fungi, impetigo, and cellulitis.
Environmental Factors: Direct exposure to sun, pollution, or extreme weather may cause sunburn, skin cancer, and rosacea.
Lifestyle Choices: Poor diet, smoking, and lack of sleep can provoke diseases in the skin such as acne and premature aging, as well as other chronic skin ailments.
Autoimmune Disorders: Diseases such as psoriasis and lupus are actually autoimmune disorders whereby the skin’s immune system mistakenly assaults healthy skin cells.
3. Symptoms of Skin Diseases
Even though each individual skin condition has its own separate symptoms, some common indicators to look out for include:
Itching or burning: The most common cause of this is eczema, psoriasis, and hives.
Rash or redness: Most allergic reactions present as red and inflamed skin, which is also seen in eczema and rosacea.
Bump or blister: Acne, chickenpox, and cold sores cause small bumps and blisters on the skin.
Color change: These are the skin conditions; they might be vitiligo, melasma, or fungal infections changing the color of the area to be lighter or darker.
Dry or Scaly Skin: Psoriasis, eczema, and other chronic conditions often cause patches of dry, flaky skin.
Pain or Tenderness: Skin infections like cellulitis and shingles can cause areas of skin to become painful or tender to the touch.
Changes in Moles: Skin cancer can sometimes be detected early by observing changes in moles, such as asymmetry, uneven borders, or unusual colors.
4. Diagnosis of Skin Diseases

To diagnose the skin diseases accurately, a dermatologist typically employs several techniques:
Physical Examination: The doctors check the color and texture of the skin, nails, and hair.
Patch Testing: This tests for allergic reactions by putting small amounts of substances on the skin.
Biopsy: If one suspects that there is some form of skin cancer or other severe conditions, they take a small tissue sample under the microscope.
Blood tests: used to detect autoimmune dermatosis. It tests the level of certain antibodies in the blood.
5. Treatment Plans for Dermatologic Conditions
Treatment for a dermatologic condition is based on the underlying cause, type, and extent of the disease condition. Here is a general overview of some of the common treatments:
Topical drugs: eczema, acne, and psoriasis are treated with topical creams, ointments, or gels containing corticosteroids, retinoids, or antibiotics.
Oral medications: In cases of serious skin diseases, like systemic infections or autoimmune-related disorders, oral antibiotics, antihistamines, or immunosuppressants may be prescribed.
Phototherapy: Psoriasis and eczema are treated with UV light therapy. This treatment reduces inflammation and slows the rate of turnover of skin cells.
Surgery or Cryotherapy: Some types of skin cancers, warts, and cysts may need surgical removal or cryotherapy, a procedure where liquid nitrogen is used to freeze abnormal tissue.
Moisturizers and Emollients: Applying moisturizers on a daily basis can help to reduce eczema symptoms, as it hydrates the skin and makes the skin barrier stronger.
Lifestyle and Diet Changes: For those suffering from acne, eczema, or rosacea, lifestyle and diet changes such as avoiding identified allergens, eating healthy, and reducing stress may limit flare-ups.
Alternative Medications: While some patients do well by using alternative medications such as aloe vera, tea tree oil, or oatmeal baths, caution and especially under a doctor’s recommendation are advised.
6. Prevention of Skin Diseases
Skin diseases cannot all be prevented, but there are means of protecting oneself from most of them.
Skin Protection: Applying broad-spectrum sun protection daily, including during winter, helps cut down on chances of sunburn, skin aging, and skin cancer.
Healthy Lifestyle: A nutritious diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking can help protect the skin.
Avoidances of allergens or irritants: This is by ensuring that clients who have sensitive skin refrain from using products with abundant chemical and fragrance presence in order to avoid an outbreak and irritation.
Hand hygiene: This is by ensuring that hands are being washed as a way to curb the spread of pathogenic skin diseases in hospitals.
Conclusion

There are numerous kinds of skin diseases, presenting great variability in cause, severity, and impact. Most of them can be pretty well managed if diagnosed in time and appropriate treatment is received. It’s knowledge on the various kinds, their causes, symptoms, and treatments that aids proactive measures and protects the skin in pursuit of enhanced appearance and health. Whether through prevention or treatment, the issue of skin health is necessary for maintaining wellness and a good quality of life. Even if you are experiencing any kind of persistent skin symptom, you should always consult with a dermatologist to ensure getting a proper diagnosis and care.



