All skin allergies are a common problem in children and severely disturb their lives and comfort. Allergic reactions can show through rashes, hives, or itching. All allergies are caused by substances. The causes, types, disadvantages, and treatments of skin allergies in children need to be known for effective management.
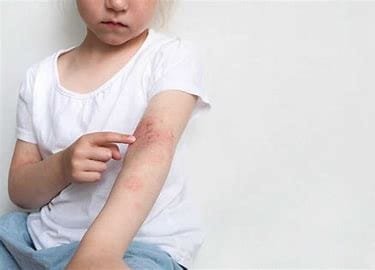
Causes of skin allergies in children
Several environmental and genetic influences contribute to the root cause of skin allergies in children.
The following are the main causes:
Environmental Allergens:
These include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold that cause allergic reactions in children. These common allergens are said to cause conditions like eczema or allergic contact dermatitis.
Food allergies:
Some familiar examples of a food allergy among children include milk, eggs, peanuts, and shellfish. It usually manifests as hives, rashes, or swelling around the face and the lips.
Chemical Irritants:
Products containing chemicals can cause an allergic reaction, including detergents, soaps, lotions, and even certain fabrics. These generally cause direct irritation to the skin, resulting in conditions such as contact dermatitis.
Insect Bites or Stings:
Children are allergic to the venom of insects, which can include bees, wasps, or ants. This can result in local swelling, redness, or can be more dangerous and cause hives, with anaphylaxis rarely occurring.
Genetics:
If there is a history of allergies, asthma, or eczema in the family, the child will probably develop skin allergies. Susceptibility increases if there is a family history of allergic conditions.
Types of Skin Allergies in Children
There are several common skin allergies that children suffer from. Knowing the different types will make it possible for parents to give due care to their child.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Eczema is actually the most common skin condition in children. It causes dry, scaly, and itchy patches of the skin, which may occur on the face, hands, or back of the knees. More often than not, eczema is an allergic reaction that may result because of sensitivities to allergens or irritants such as wool, harsh soap, or even a change in temperature.
Hives (Urticaria):
Hives are itchy raised welts that may appear red. They are very sudden. Most often they occur with an allergic reaction, such as to food, medication, or environmental allergens. Hives tend to last for a few hours or less. Sometimes not.
Contact Dermatitis:
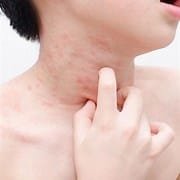
This condition may result when the child’s skin directly comes into contact with an irritant or an allergen. Contact dermatitis leads to redness, blistering, or peeling of the skin. The causes include, among others, nickel found in jewelry, certain plants like poison ivy, and chemicals in certain household products.
Allergic Rhinitis with Skin Manifestations:
Some children with allergic rhinitis, which is more common and known as hay fever, also have skin manifestations like rashes or itching. These may be with sneezing, a runny nose, or watery eyes.
Diseases Associated with Childhood Skin Allergies
Generally, children with allergies face many problems. Because these allergies do not threaten life, they can dramatically change the quality of life of the child.
Discomfort and Irritation:
An itchy child would never rest or sleep. The constant itching and irritation may cause a lot of harm to the affected parts, and infection may be one of them as well.
Social and emotional impact:
Rashes or hives may lead to a decrease in self-confidence or extreme discomfort in the social life of children, especially in school. The child may become worried about his/her appearance or find himself isolated due to his/her illness.
Interference with Normal Day-to-Day Activities.
Allergies often interfere with normal day-to-day activities such as engaging in outdoor games, taking part in sports, or even wearing certain clothes. This interference often affects the child’s physical and psychological development.
Potential Risk of Infections.
Rubbing with hands causes damage to skin; rashes or hives can become open wounds and therefore are more vulnerable to bacterial infections. These infections could then proceed to complicate the condition and hence require additional medical procedures.
Treatment of skin allergies in children
Once a skin allergy in a child has been diagnosed, management would involve identification of triggers, which actually includes avoiding allergens, as well as the use of appropriate treatments to help relieve symptoms.
Avoiding Triggers:
Actually, the best form of management of skin allergy is actually the identification and avoidance of known triggers, which may include hypoallergenic laundry detergents, the removal of dust mites, and foods, among others.
Topical Medications:
If eczema or contact dermatitis is present, then physicians and pediatricians prescribe topical corticosteroids or creams to help alleviate inflammation and itchiness. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams can also be used to treat mild skin irritation.
Antihistamines:
Oral antihistamines are used in the treatment of itches, hives, and other allergic reaction symptoms. They are most helpful in the case of hives or allergic rhinitis that involves certain manifestations of symptoms on the skin.
Moisturizing:
This is one of the most basic needs of children affected by eczema. The skin should always be moisturized to prevent it from becoming dry and irritated. Thick emollient creams or ointments moisturize the skin by locking moisture within, thereby creating a sort of barrier on the skin, which prevents the skin from becoming dry and irritated.
Allergy Testing and Immunotherapy:
A doctor may also refer allergy testing to evaluate the specific allergens responsible for the negative reactions. Immunotherapy, allergy shots, or sublingual tablets may be prescribed in order to induce long-term relief against environmental allergens.
Cold Application:
Applying cold compresses directly to the area where the skin feels itchy or swollen will make a person feel better for that short duration. Cold packs reduce inflammation and ease the pain caused to the skin.
Conclusion
Skin allergies in children are manageable if proper understanding, prevention, and treatment are achieved. Early detection of triggers and the implementation of practical working strategies should contribute the most to a child’s improved quality of life. Parents, therefore, need close co-working with the pediatrician or allergist so as to be able to provide quality care for their child and facilitate more comfort and allergy-free life for the child.



