The term “metabolic foods” has become popular over the past two years or so—consider them to be food items that boost one’s metabolism and cause the body to burn its stored fat much better. As people wish to live healthy lives and bring their weight under their control naturally, along with gaining more energy, these foods have been under focus. But what are these metabolic foods, and what is their mechanism? In this article, we’ll discuss the characteristics of metabolic foods, the health benefits associated with consuming them, and how you can add them to your diet for long-term health benefits.
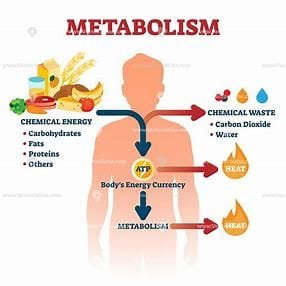
What is metabolism?
In order to understand what metabolic foods are, first of all you need to know what metabolism is.
Metabolism describes the process by which your body takes in what you eat and drink and breaks this down into usable energy. This energy, then, will go on to power everything from cellular functions to your own physical activity. The faster that metabolism is, the higher the amount of calories burned at rest.
Conversely, a slower metabolic rate may result in weight gain as well as lethargy.
Metabolic rate varies in everyone and depends on so many factors, including age, sex, muscle mass, and physical activity. However, some foods can boost your metabolic boost to burn more calories that will, over time, help with managing your weight.
Key Qualities of Metabolic Foods
Metabolic foods share certain qualities.
Even though they are not magical, they possess properties, either enhancing processes to burn calories or promoting the good utilization of energy. Here are some of the essential characteristics that qualify a food as “metabolic”:
Rich in Protein:
A macronutrient requires more energy to be digested than fats or carbohydrates. This is referred to as the thermic effect of food (TEF). High-protein-containing foods such as lean meats, eggs, and legumes can be useful for metabolism since it takes more energy for your body to break them down.
Additionally, protein supports muscle mass that boosts your BMR—the calories your body burns at rest.
High in Fiber:
This diet further includes fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. High-fiber foods promote longer satiety and reduce excessive intake during overeating. Furthermore, it costs more energy to the digestive system to process fiber compared to other materials, implying higher calorie burn. Insoluble fiber further contributes to an improvement in gut health, which is related to better metabolic function.
Thermogenesis:
Certain foods are indeed thermogenic—they briefly increase your body’s internal temperature, which can activate your metabolism to perform more. Some examples of thermogenic foods include chilies—they contain capsaicin, a proven compound that provokes thermogenesis. Ginger, turmeric, and cinnamon may also raise your body temperature to burn higher amounts of calories.
Rich in Good Fats:
Now, this sounds completely bizarre, but some fat, and specifically omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are essential in the running of a healthy metabolism. The good fats in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds also help to regulate insulin levels and reduce inflammation, which are both important processes to maintain a healthy metabolism.
Low GI:
Low GI foods are slow-digestible foods that cause no steep rise in blood sugar. An example of low-GI foods includes beans and lentils or leafy greens, which will not let your blood sugar spike. The blood sugar must remain steady to keep metabolism constant all day long. When the blood sugar spikes, it brings with it an increase in insulin that tells your body to store fat. Metabolic food helps prevent this process and keeps metabolism running smoothly.
Benefits of Having Metabolic Food in Your Diet
Metabolic foods are not just for calorie burners. They have a lot of other benefits that improve one’s general health, boost energy levels, and maintain the body within a healthy weight.

Here are some of the major benefits of regular consumption of metabolic foods:
High Calorie Burning:
The effects of metabolic foods are usually very low, yet they can help in burning more calories over a period of time. When taken with a well-balanced diet and regular exercise, metabolic foods enable you to either lose or maintain weight without having radical lifestyle changes.
Stable Blood Sugar:
Most metabolic foods, especially those that are high in fiber and of low glycemic index, tend to support stable blood sugar levels. This prevents low energy crashes and reduces the possibility of developing insulin resistance, a common condition associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Improved Energy Levels:
Metabolic foods stabilize blood sugars and ensure a steady release of energy. This increases your general levels of metabolic energy; thus, you feel more active and tend to exercise more, which contributes to increasing your metabolic rate.
Increased Muscle Mass:
Protein-rich foods support building muscle and the repair of muscle. Since a certain amount of muscle indeed burns more calories than fat, having more lean muscle mass can contribute to a higher basal metabolic rate, even when you are not working out.
Improved Digestive Health:
one of the main features of the metabolic foods is that they help in digestion by promoting healthy bowel movements and preventing constipation. Overall health of the digestive system means your body works fine to process nutrients, which in turn supports optimal metabolism.
How to Include Metabolic Foods in Your Diet
To incorporate metabolism-boosting foods into your diet does not prove to be so difficult, as there are many simple ways of doing this. To illustrate, start from your breakfast: an egg, Greek yogurt, or oatmeal is a pretty decent high-protein, fiber-rich meal that will get started your metabolism in the morning.
Snack smart:
Replace your chips or sweets with nuts, seeds, or a piece of fruit. These will not only put an end to your hunger but also trigger your release of energy at a slow and steady tempo.
Spice it up:
Sprinkle spices such as cayenne pepper, turmeric, or cinnamon on your meals, as these are proven to be thermogenic, which helps raise your metabolism calorie count additively.
Focus on whole foods:
Most of the time, you should be using whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and even lean proteins. Try to avoid as much processed food as possible because it is mostly devoid of nutrients and slows down your metabolism.
Hydrate:
Water is to run metabolism. Your body needs cold water because it increases your metabolism for a short time due to the warming-up process that occurs in bringing it up to the temperature that is present in your body.
Conclusion
While no single food accelerates metabolism to significant degrees, overall, metabolic foods can collectively influence how well your body is burning calories. Focus on protein-rich and fiber-dense and thermogenic foods, paired with healthy fats and low-GI foods, and you’ll end up improving not only your metabolic rate but generally, your health. Like with any food-related change, it should be combined with a well-balanced diet and regular exercise and hydration for better results.





Pingback: "7 Alarming Facts About Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals"/pharmaexplain.com