Introduction

Brain fog is a general term, which refers to some pattern of symptoms related to cognitive activity. It is not related to a proper medical condition like dementia or cognitive impairments. Rather, it describes an individual’s experience, and that is when they feel that their mind is moving with a slow motion, or they are unable to stay concentrated and focused. People with brain fog usually point out confusion, forgetfulness, or distraction, which hampers their ability to focus on a task and therefore accomplish it efficiently. This condition may be temporary, but in some cases, it may last for very long periods.
Causes of Brain Fog
Lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and mental health can cause brain fog. For example, some of the common causes include:
Poor Sleep: You require sleep for cognitive activity. In case you have not slept well, the brain is unable to digest any information and gain focus, leading one to be in a dazed mode.
Stress: High stress levels affect your brain directly by affecting memories, concentration levels, and one’s ability to take proper decisions.
Diet and Nutrition: The diet, if unbalanced, can lead to inadequate intake of necessary nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, and this would negatively affect brain function.
Medical Conditions: Hypothyroidism, chronic fatigue syndrome, and autoimmune diseases often cause brain fog as part of the symptomatology. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can lead to cognitive sluggishness.
Medications: Some drugs have effects on the central nervous system that lead to cognitive impairment. For instance, antibiotic overdose may cause disruptions of gut health and, by extension, affect brain functions.
Mental Disorders: Anxiety and depression cause impairments in cognition because of their ability to disturb concentration, memory, and decision-making capabilities—all characteristics of brain fog.
Brain fog symptoms
Brain fog is a cognitive symptom that has a whole range of symptoms that affect the daily life and mental well-being of an individual. The most common symptoms are:
Lack of Clarity: A feeling of mental fuzziness or haziness that prevents clear thinking.
Poor Memory: Failure to recall recent events, conversations, or names.
Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing on tasks, which can lead to frustration and decreased productivity.
Mental fatigue: a persistent feeling of tiredness, even after sufficient rest.
Confusion and Disorientation: The inability of gathering thoughts or clear orientation
Most people are then subjected to the feeling that they do not feel themselves as well. Helplessness and frustration are therefore manifested too.
Brain fog consequences on human life
The life of human beings is bound to be severely suffered at both the workplace, school, and college levels, as well as in interpersonal and psychological lives. This is done in various ways. Below are some discussions of some of these aspects:
1. Work or school productivity

This is because brain fog impairs the execution of duties that require attention, focus, and critical thinking. Sometimes, a person suffers from brain fog, meaning one will read the same paragraph several times with an inability to understand the talk that occurs in a meeting. Low productivity often emanates from this, giving a sense of frustration to job dissatisfaction. For students, it may lead to poor academic performance due to failure to recall information or perform well in tests.
2. Effects on Relations
Cognitively, brain fog may strain personal relationships. A mentally unfocused person or someone unable to remember some important detail may seem uninterested or even disconnected. Others may misunderstand the behaviors as a lack of interest or emotional distance. This will cause hurt feelings and misunderstandings. People suffering from brain fog will have less mental energy to participate in social activities, which can make them withdraw more.
3. Impact on Mental Health:
Brain fog might compound the already widespread mental condition or even trigger fresh ones. One’s inability to concentrate or even remember material can become frustrating, futile, and stressful. The feelings can progress to develop anxiety and depression. Those with a long-term diagnosis of brain fog often find themselves asking about their own minds, and their self-esteem and self-confidence start running low.
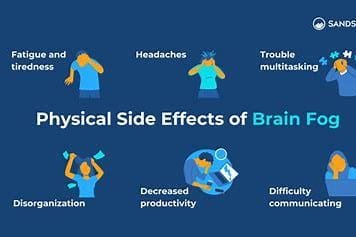
4. Physical Consequences of Brain Fog
Sometimes, brain fog may be a sign of deeper health issues, including poor diet, sleep deprivation, or chronic stress. If left unaddressed, these problems can cause long-term health issues, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, and a weakened immune system. Additionally, physical fatigue usually accompanies brain fog, which can further reduce motivation to exercise and lead a healthy lifestyle, thereby forming a vicious cycle of unhealthy living.
Brain Fog Management
This would mean a holistic approach in terms of lifestyle and mental health, such as:
Sleep: Good sleep habits would be maintained by keeping constant sleep schedules, which helps in the improvement of function in the brain.
Stress reduction: Mindfulness or any relaxation technique can get rid of the mental clutter that aggravates brain fog.
Nutrient-rich diet: It is proven to be good for the health of the brain and provides better clarity and focus.
Exercise: The general report has been of improving mood and cognitive functions through exercise.
Seek advice from a medical doctor: A doctor may be able to diagnose a medical condition if the condition persists.
Conclusion
Most commonly, brain fog symbolizes a rather unpleasant experience, thereby challenging almost every aspect of living. Although it may seem like a nonspecific condition and has no specific medical definition, its symptoms are more than likely very real; after all, the impact it could be having on everyday life, mental well-being, as well as personal relationships, may be serious enough to at least warrant some sort of seriousness being taken. Fortunately, such an experience can sometimes either be controlled or even evened out by the taking of proactive measures for self-care or suitable medical assistance.



